Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Kosin Med J > Volume 32(2); 2017 > Article
-
Case Report
A Case of Primary Tracheal Schwannoma - Sung Min Choi, Ji Hong You, Sang Bae Lee, Seong Han Kim, Yon Soo Kim
-
Kosin Medical Journal 2017;32(2):258-262.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.258
Published online: December 29, 2017
Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Sung Min Choi, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, 211 Eonju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06273, Korea. Tel: +82-2-2019-6236, Fax: +82-2-3462-0129, gomdanism@yuhs.ac.kr
• Received: May 8, 2016 • Revised: May 13, 2016 • Accepted: August 10, 2016
Copyright © 2017 Kosin University College of Medicine
- 1,029 Views
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- Although benign nerve sheath tumors have been described, primary tracheal schwannomas are extremely rare. We report a case of primary tracheal schwannoma, a rare benign nerve sheath tumor in a 58-year-old man with atypical symptoms of chronic cough, sputum and dyspnea for 2 months. Chest computerized tomography showed a 1.7 cm polypoid lesion in posterior wall of mid trachea. The results of bronchoscopic biopsy and immuno-histo-chemical studies were consistent with schwannoma. A surgical treatment of tumor resection and tracheal reconstruction by end-to-end anastomosis was performed.
- A 58-year-old man was referred to our institution because of chronic cough, sputum and shortness of breath since 2 months ago. In his past medical history, he had been treated for pulmonary tuberculosis 30 years ago and he had no recurrence till date. He had smoked a pack of cigarettes per day for the last 25 years. Physical examination was normal except mild stridor in auscultation. Laboratory tests and chest x-ray were normal except post inflammatory scar in left upper lung field (Fig. 1A). Chest computerized tomography (CT) revealed a 1.7 cm polypoid lesion in posterior wall of the mid trachea (Fig. 1B). Flexible bronchoscopy confirmed the presence of a 2 cm, round, polypoid endotracheal lesion at 3 cm above the carina and a forcep biopsy was taken (Fig. 1C). The lesion was localized only in mid trachea without any evidence of esophageal invasion on endoscopic trans-esophageal ultrasonography (Fig. 1D). Flow-volume curve of pulmonary function test (PFT) revealed upper airway obstructive pattern with inspiratory plateau (Fig. 2A). Forced vital capacity (FVC) was 3.85 liters (L), 110% of reference vital capacity estimated by sex, age and height. Forced expiratory volume during the first second (FEV1) was 2.27 L, 88% of reference. FEV1/FVC was 59%, meaning obstructive lung disease. Histo-pathologic study revealed a schwannoma and the tumor showed proliferation of spindle cells with elongated nuclei arranged in palisading pattern in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (Fig. 2C), and showed positive S-100 staining in immuno-histo-chemical study (Fig. 2D). A surgical treatment was performed with posterolateral thoracotomy, complete resection of the tumor involving regional trachea and tracheal reconstruction by end-to-end anastomosis. The gross specimen of the tumor was 2.1 × 1.8 × 1 cm sized yellowish hard mass, encapsulated with connective tissue. The histo-pathologic and immuno-histo-chemical findings were consistent with schwannoma, as previously proven. Tracheal resection margins and para-tracheal lymph nodes were free from tumor. At 6 months after surgery, PFT was done and the result showed normal flow-volume curve with FEV1/FVC 77% (Fig. 2B). On postoperative serial follow up examinations, chest CT and bronchoscopy, of 6 months, 1 year and 2 years, no recurrence was detected.
CASE
- Neurogenic tumors are divided into nerve sheath tumors and neurofibromas by their histo-pathologic features and the existence of nerve axon.4 Nerve sheath tumors have no axon, and are categorized as schwannomas (neurilemmoma) and non-schwannian nerve sheath tumors.4 Schwannomas of the trachea arise from intra-luminal neurogenous tissue, more precisely, schwann cells of the nerve sheath.5 On the other hand, neurofibromas consist of all elements of nerve including schwann cells, perineural cells and axons.4
- The signs and symptoms are nonspecific and depend on the size and location of tumor and degree of airway obstruction. Cough, wheezing and dyspnea caused by obstruction of airway are most common, while hemoptysis, hoarseness and chest pain are less frequent.2 The patient presented in this case also suffered from cough, stridor and dyspnea as symptoms of airway obstruction.
- Since tracheal schwannoma is rare and nonspecific symptoms are associated with it, preoperative diagnosis is difficult. Imaging studies can be used to detect the disease. Chest x-ray is not an efficient radiologic modality because of the superimposed soft tissues and bony structures. Chest CT is a useful radiologic option in defining the size, location and extension of the disease. However, it is usually difficult to make differential diagnosis of tracheal tumors by radiologic characteristics of chest CT images.3 A biopsy is required to make differential diagnosis of the tumor by pathology and bronchoscopic examination is a useful method to take biopsy specimens. As noted above, our patient underwent chest x-ray, but there was no suspicious finding of endotracheal lesion, while chest CT image revealed its existence.
- In histo-pathology of H&E stain, schwannoma has characteristic structural patterns of highly cellular regions (Antoni A) and loose paucicellular regions (Antoni B).3 Tumor cells in Antoni A are closely packed forming palisades and have spindle-like morphology with club-shaped nuclei.3 Within Antoni A regions, bands of fusiform nuclei alternated with clear zones devoid of nuclei are called Verocay bodies.3 In immuno-histo-chemical study, schwannoma shows positivity for S-100 protein, and this can be used to confirm the diagnosis of schwannoma.3 Pathologic features, such as Antoni A, Antoni B, Verocay body and S-100 positivity, were also shown in our case.
- Despite benign feature of primary tracheal schwannoma, it has to be removed to prevent lethal suffocation caused by airway obstruction. Tracheal schwannomas have been removed by operative tracheal resection with tracheal reconstruction or bronchoscopic resection.6 The choice of treatment should be influenced by the patient's general condition, comorbidity, bronchoscopic presentation of the tumor, the risk of tracheal resection and the presence of extra-tracheal component. For patients with large, sessile tumor and without reduced cardio-pulmonary function, operative resection is essential as a ultimate treatment method.2 In case of pedunculated and intraluminal tumors, or in patients with severely reduced underlying cardio-pulmonary function, bronchoscopic resection can be a proper option.2 However, bronchoscopic resection of tracheal schwannoma has the risk of recurrence. In the literatures reviewed between 1950 and 2015, there were 3 cases of local recurrence in the patients who had been treated by bronchoscopic resection.378 In the report of Horovitz AG et al, tracheal schwannoma witch had been removed by bronchoscopy, recurred 12 years after the procedure.8 In the present patient, there was no co-existent cardio-pulmonary disease, and thus surgical resection was performed to avoid recurrence.
- In conclusion, primary tracheal schwannoma is a rare benign neoplasm and may cause atypical symptoms. Therefore, it is important to have clinical impression and perform accurate examinations for avoiding occasional mistaken diagnoses. Chest CT is a useful tool for the detection of the disease, but has nonspecific manifestations. Bronchoscopic evaluation is recommended for differential pathologic diagnosis. After diagnosis, a proper treatment method has to be chosen with careful consideration of the patient's underlying condition. Prognosis of primary tracheal schwannoma is favorable with low recurrence rate. However, as the longest recurrence period, previously reported, was 12 years, long term imaging follow up and bronchoscopic surveillance of tumor recurrence at 5, 10 and 15 years may be required additionally.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Isaac BT, Christopher DJ, Thangakunam B, Gupta M. Tracheal schwannoma: Completely resected with therapeutic bronchoscopic techniques. Lung India 2015;32:271–273.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Ge X, Han F, Guan W, Sun J, Guo X. Optimal treatment for primary benign intratracheal schwannoma: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett 2015;10:2273–2276.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Jung YY, Hong ME, Han J, Kim TS, Kim J, Shim YM, et al. Bronchial schwannomas: clinicopathologic analysis of 7 cases. Korean J Pathol 2013;47:326–331.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Rusch VW, Schmidt RA. Tracheal schwannoma: management by endoscopic laser resection. Thorax 1994;49:85–86.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Righini CA, Lequeux T, Laverierre MH, Reyt E. Primary tracheal schwannoma: one case report and a literature review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2005;262:157–160.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Takeda K, Horiuchi M, Nakaya M, Yamaguchi K, Fujikawa A. Schwannoma of the trachea; a new resection technique. Auris Nasus Larynx 2003;30:425–427.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Kasahara K, Fukuoka K, Konishi M, Hamada K, Maeda K, Mikasa K, et al. Two cases of endobronchial neurilemmoma and review of the literature in Japan. Intern Med 2003;42:1215–1218.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Horovitz AG, Khalil KG, Verani RR, Guthrie AM, Cowan DF. Primary intratracheal neurilemoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1983;85:313–317.ArticlePubMed
References
Fig. 1

Imaging studies of tracheal schwannoma. (A) Chest x-ray showed only a scar change of previous pulmonary tuberculosis in left upper lung field.(B) Computed tomography revealed a round-shaped 1.7 cmpolypoid lesion in mid trachea.(Arrow) (C) Bronchoscopic evaluation showed a polypoid endotracheal mass lesion. (D) Endoscopic trans-esophageal ultrasonography showed that this lesion was localized only in trachea without any evidence of esophageal invasion. (Arrow)

Fig. 2
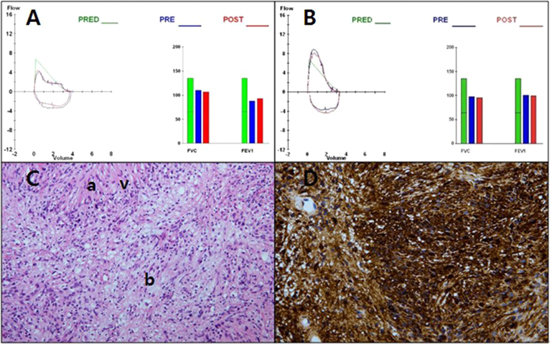
Flow-volume curves of pulmonary function test (PFT) and histo-pathologic pictures of tracheal schwannoma. (A) Preoperative flow-volume curve of PFT revealed upper airway obstructive pattern with inspiratory plateau. Forced vital capacity (FVC) = 3.85 liters (L), 110% of reference. Forced expiratory volume during the first second (FEV1) = 2.27 L, 88% of reference. FEV1/FVC = 59% (B) Postoperative flow-volume curve of PFT showed normal flow-volume curve. FVC = 3.36 L, 97% of reference. FEV1 = 2.6 L, 101% of reference. FEV1/FVC = 77% (C) In hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, cellular region (Antoni A)(a) and loose paucicellular region(Antoni B)(b) were documented. Verocay body(v) with palisading elongated nuclei was also seen. (Magnification, ×200)(D) Immuno-histo-chemical S-100 staining of this lesion had strong positivity. (Magnification, ×400)

Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Primary tracheal schwannoma: Bronchoscopic management of a rare tracheal tumour
Krizelle Acibal, Belgundi Preeti Vidyasagar, Harikishan Gonuguntla
Respirology Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef

 KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite


