Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Kosin Med J > Volume 33(3); 2018 > Article
-
Original Article
Clinical features of Epstein-Barr Virus-associated Infectious Mononucleosis According to Age Group in Children - Soram Lee1, Ju-Young Chung2, Jung Je Park3, Ji-Hyun Seo1, Jae Young Kim4, Jung Sook Yeom1, Eun-Sil Park1, Jae-Young Lim1, Hyang-Ok Woo1, Hee-Shang Youn1
-
Kosin Medical Journal 2018;33(3):347-357.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2018.33.3.347
Published online: January 19, 2018
1Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Jinju, Korea
2Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Otolaryngology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Jinju, Korea
4Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang National University Hospiratal, Changwon, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Ji-Hyun Seo, Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, 79, Gangnam-ro, Jinju-Si, Gyeongsangnam-do 52727, Korea Tel: +82-55-750-8731 Fax: +82-55-752-9339 E-mail: seozee@gnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2018 Kosin University School of Medicine Proceedings
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,286 Views
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- Few studies of pediatric Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated infectious mononucleosis (IM) have been conducted in Korea. We evaluated the clinical features of children with IM to define differences according to age.
-
Methods
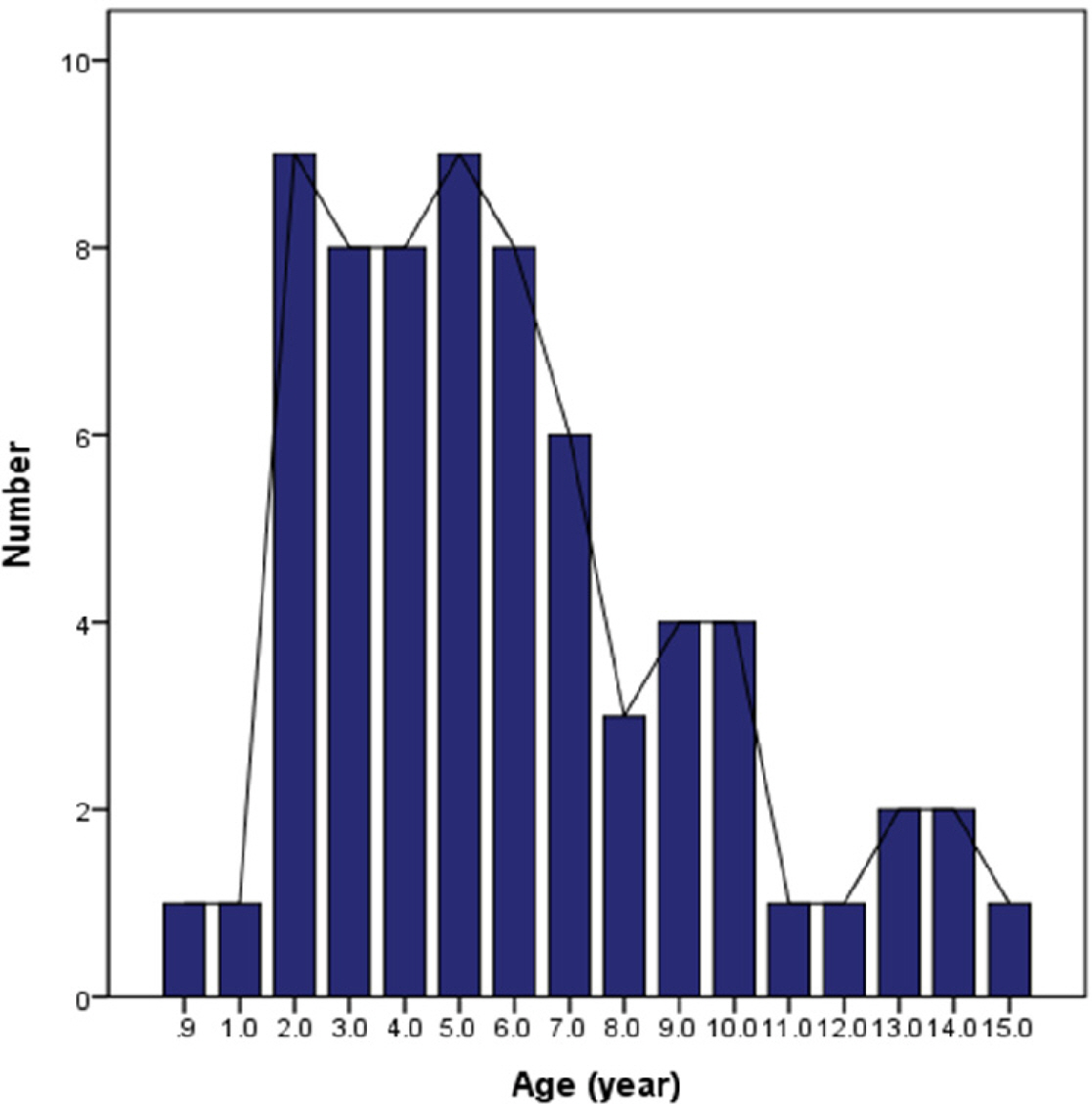
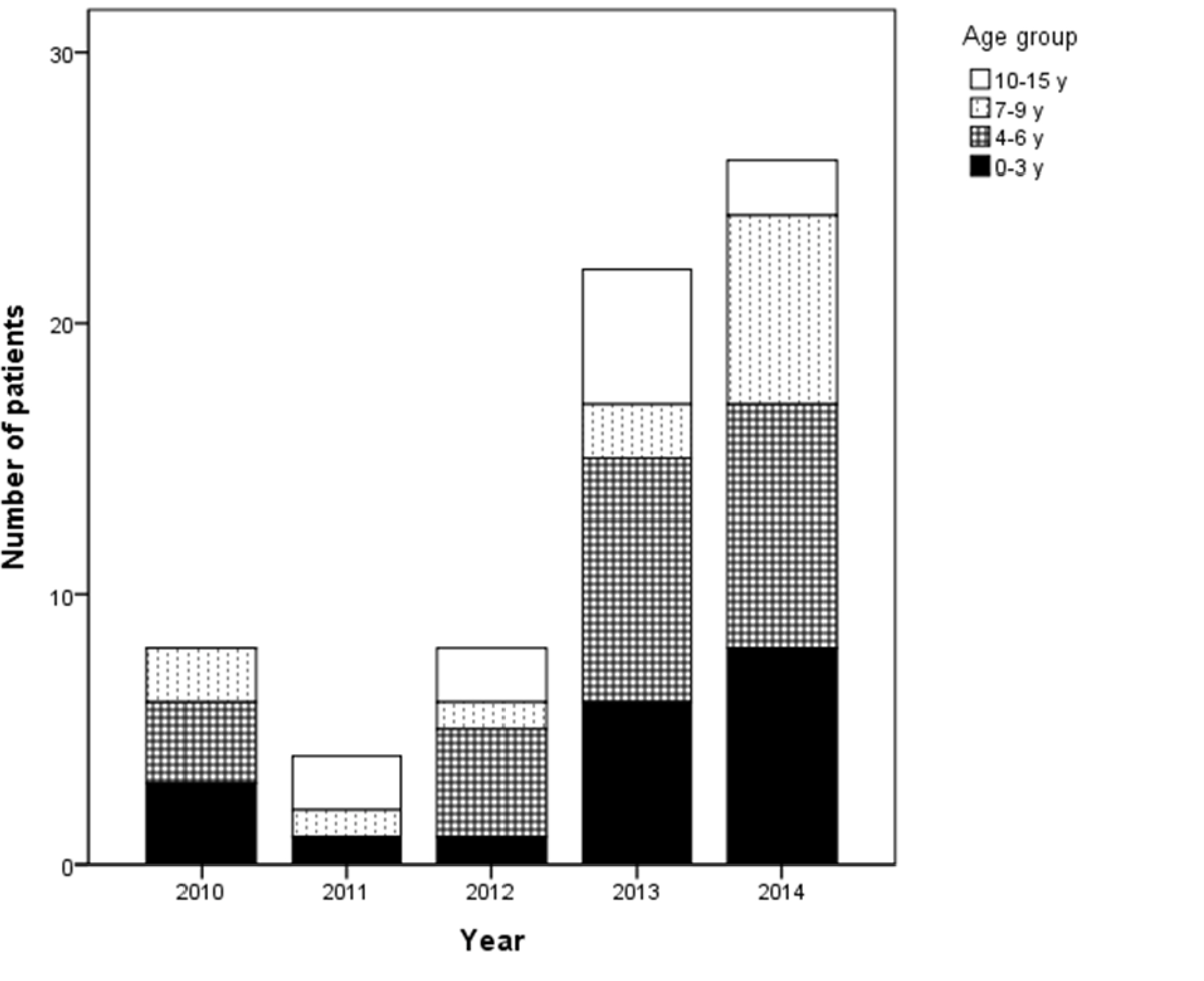
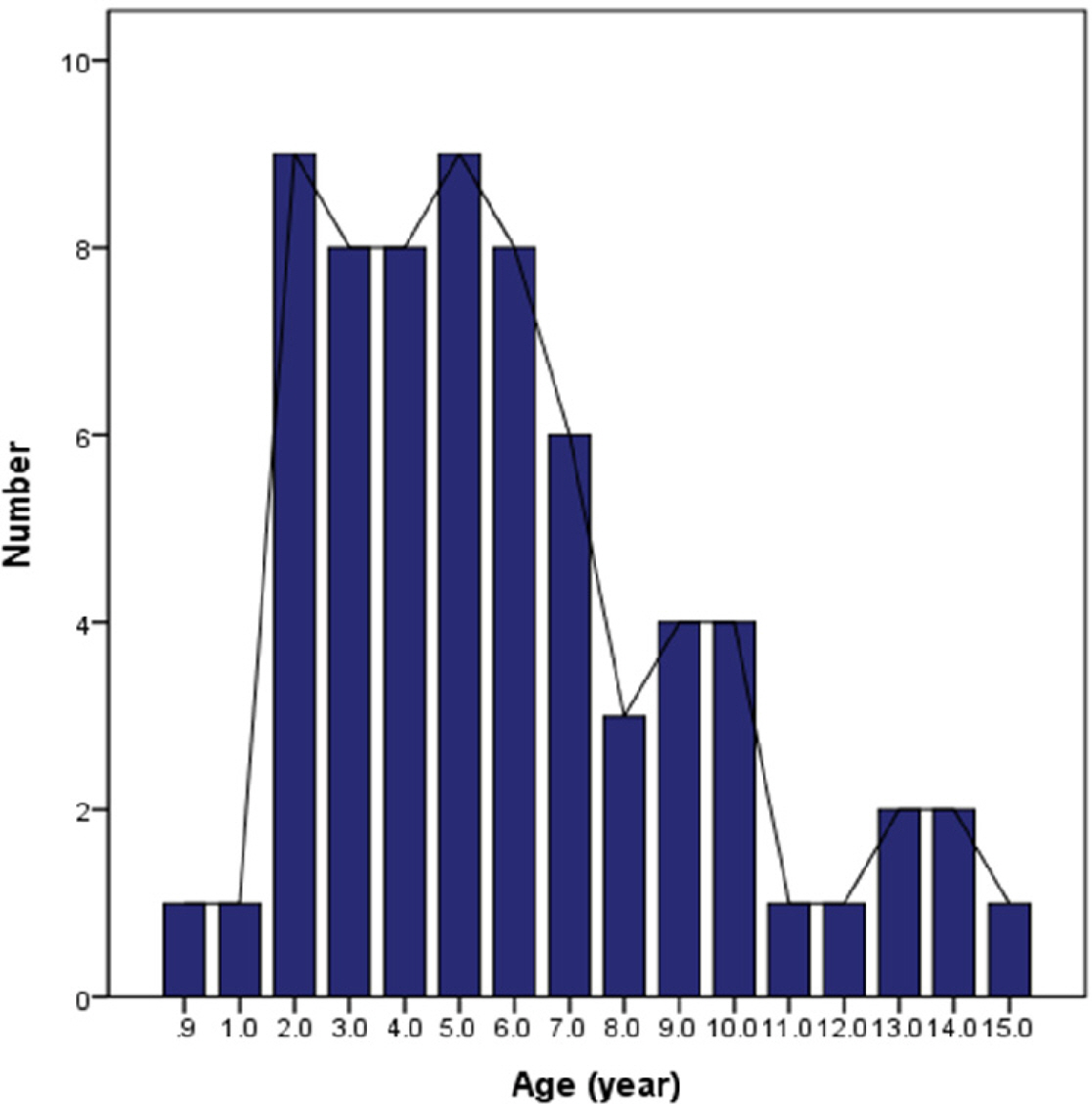
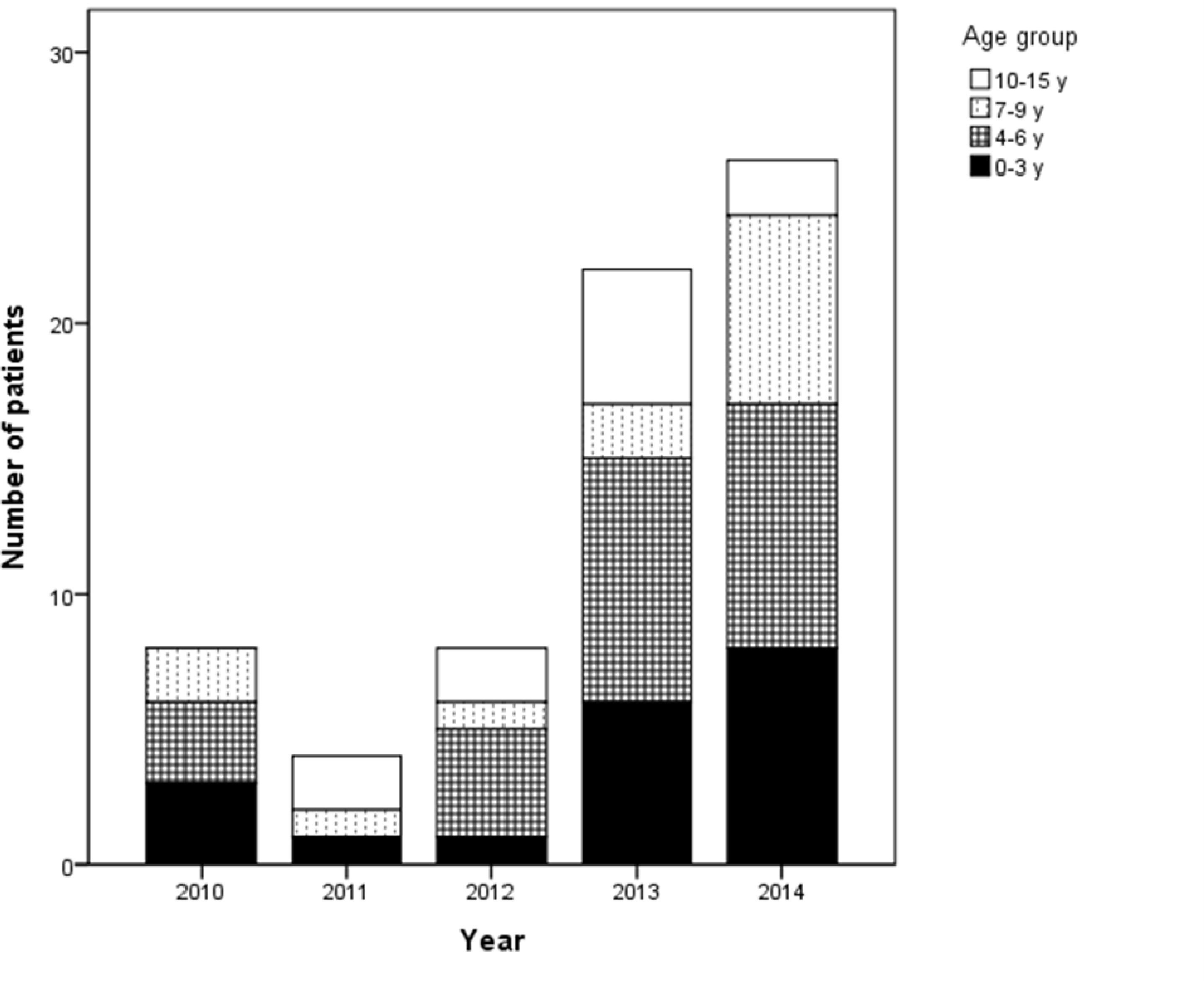
- We conducted retrospective chart reviews of 68 children aged 0 to 15 years who were diagnosed by EBV-associated IM with EBV-Viral Capsid Antigen(VCA) IgM at laboratory test and were admitted between 2010 and 2014. The children were classified into four age groups: aged 0–3, 4–6, 7–9, and 10–15 years.
-
Results
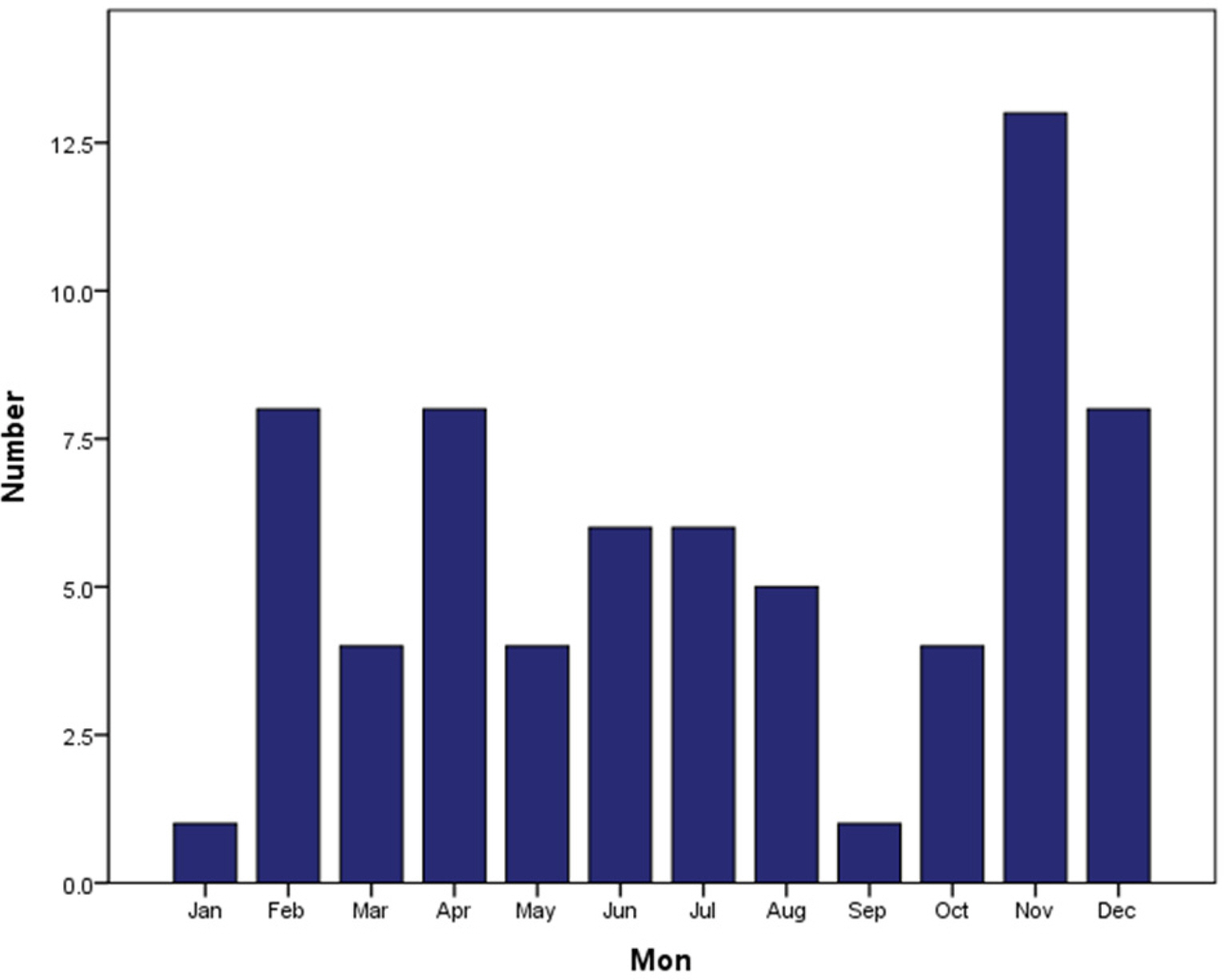
- The age distribution of patients was as follows: 19 (27.9%) 0–3, 25 (36.8%) 4–6, 13 (19.1%) 7–9, and 11 (16.2%) 10–15. Fever was the most common presentation regardless of age. It was more common in the 0–3 group than the 4–6 group (P = 0.018). Pharyngitis was more common in the 7–9 group than the 0–3 group (P = 0.048), and myalgia was more common in the 10–15 group than the 0–3 group (P = 0.007). Pharyngitis was accompanied by lymphadenopathy, protracted fever, and rash. In the 0–3 age group, the prevalence of rash was higher while the percentage of atypical lymphocytes was lower, but there was no statistical support for this tendency. There were no differences in the frequency of hepatosplenomegaly or laboratory findings between age groups.
-
Conclusions
- IM is not uncommon in young children and its clinical presentation varies with age. Therefore, IM should be suspected in young febrile children with pharyngitis and rash despite low percentages of atypical lymphocytes.
- 1.Higgins CD, Swerdlow AJ, Macsween KF, Harrison N, Williams H, McAulay K, et al. A study of risk factors for acquisition of Epstein-Barr virus and its subtypes. J Infect Dis. 2007;195:474–82.ArticlePubMed
- 2.Luzuriaga K, Sullivan JL. Infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1993–2000.ArticlePubMed
- 3.Bolis V, Karadedos C, Chiotis I, Chaliasos N, Tsabouri S. Atypical manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus in children: a diagnostic challenge. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2016;92:113–21.ArticlePubMed
- 4.Murata T, Sato Y, Kimura H. Modes of infection and oncogenesis by the Epstein-Barr virus. Rev Med Virol. 2014;24:242–53.ArticlePubMed
- 5.Moon WY, Oh SH, Ko TS, Park YS, Moon HN, Hong CY, et al. Infectious mononucleosis in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1994;37:822–31.
- 6.Choi JS, Kim TH, Park HY, Lim SC. Clinical analysis of infectious mononucleosis. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1997;40:914–21.
- 7.Oh SH, Lee YA, Moon WY, Ko TS, Park YS, Moon HN, et al. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) antibody in Korean children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1994;37:804–11.
- 8.Son KH, Shin MY. Clinical features of Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis in hospitalized Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2011;54:409–13.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9.González Saldaña N, Monroy Colín VA, Piña Ruiz G, Juárez Olguín H. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of infectious mononucleosis by Epstein-Barr virus in Mexican children. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:361.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10.Topp SK, Rosenfeldt V, Vestergaard H, Christiansen CB, Von Linstow ML. Clinical characteristics and laboratory findings in Danish children hospitalized with primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. Infect Dis (Lond). 2015;47:908–14.ArticlePubMed
- 11.Wang Y, Li J, Ren YY, Zhao H. The levels of liver enzymes and atypical lymphocytes are higher in youth patients with infectious mononucleosis than in preschool children. Clin Mol Heptol. 2013;19:382–8.Article
- 12.Xiong G, Zhang B, Huang MY, Zhou H, Chen LZ, Feng QS, et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in-fection in Chinese children: a retrospective study of age-specific prevalence. PLoS One. 2014;9:e99857.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13.Dowd JB, Palermo T, Brite J, McDade TW, Aiello A. Seroprevalence of Epstein-Barr virus infection in U.S. children ages 6-19, 2003-2010. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64921.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14.Gao LW, Xie ZD, Liu YY, Wang Y, Shen KL. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of infectious mononucleosis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in children in Beijing, China. World J Pediatr. 2011;7:45–9.ArticlePubMed
- 15.Odame J, Robinson J, Khodai-Booran N, Yeung S, Mazzulli T, Stephens D, et al. Correlates of illness severity in infectious mononucleosis. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2014;25:277–80.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16.Ventura KC, Hudnall SD. Hematologic differences in heterophile-positive and heterophile- negative infectious mononucleosis. Am J Hematol. 2004;76:315–8.ArticlePubMed
- 17.Balfour HH Jr, Dunmire SK, Hogquist KA. Infectious mononucleosis. Clin Transl Immunology. 2015;4:e33.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18.Balfour HH Jr, Odumade OA, Schmeling DO, Mullan BD, Ed JA, Knight JA, et al. Behavioral, virologic, and immunologic factors associated with acquisition and severity of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection in university students. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:80–8.ArticlePubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- The Nature and Clinical Significance of Atypical Mononuclear Cells in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by the Epstein-Barr Virus in Children
Olga S Fedyanina, Anna E Filippova, Olga I Demina, Olga A Zhuliabina, Dmitry S Tikhomirov, Alexander V Filatov, Tatiana A Chebotareva, Sofya A Kuznetsova
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 223(10): 1699. CrossRef

 KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite