Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Kosin Med J > Volume 30(1); 2015 > Article
-
Case Report
A Case of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Turner Syndrome - A Rum Han1, Young Ki Lee1, Hyun Yon Jung1, Jae Hyun Park1, Jung-Woo Noh1, Eun Suk Nam2
-
Kosin Medical Journal 2015;30(1):69-72.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2015.30.1.69
Published online: January 20, 2015
1Department of Internal Medicine, and Hallym Kidney Research Institute Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author:Young Ki Lee, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University, 1, Singil-ro, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul, 150-950, Korea TEL: +82-2-829-5214 FAX: +82-2-846-4669 E-mail: km2071@unitel.co.kr
• Received: February 13, 2014 • Accepted: April 23, 2014
Copyright © 2015 Kosin University School of Medicine Proceedings
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 988 Views
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- Turner syndrome is usually accompanied with various anomalies. Congenital urological and renal abnormalities are often associated with this syndrome. The occurrence of glomerulonephritis is uncommon. An 18-year-old woman showed fatigue and profound proteinuria. She had been diagnosed with Turner syndrome in her age of 15. The kidney biopsy specimen examined by light microscopy, immunofluorescence and electron microscopic examination revealed focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. This is the first case report of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in turner syndrome in South Korea.
Figure 1.Jone-silver stain reveals segmental sclerosis in two glomeruli and tubular atrophy and interstitial foam cells(A, x200). Electron microscopy displays diffuse effacement of foot processes. There is no electron dense material deposit(B).
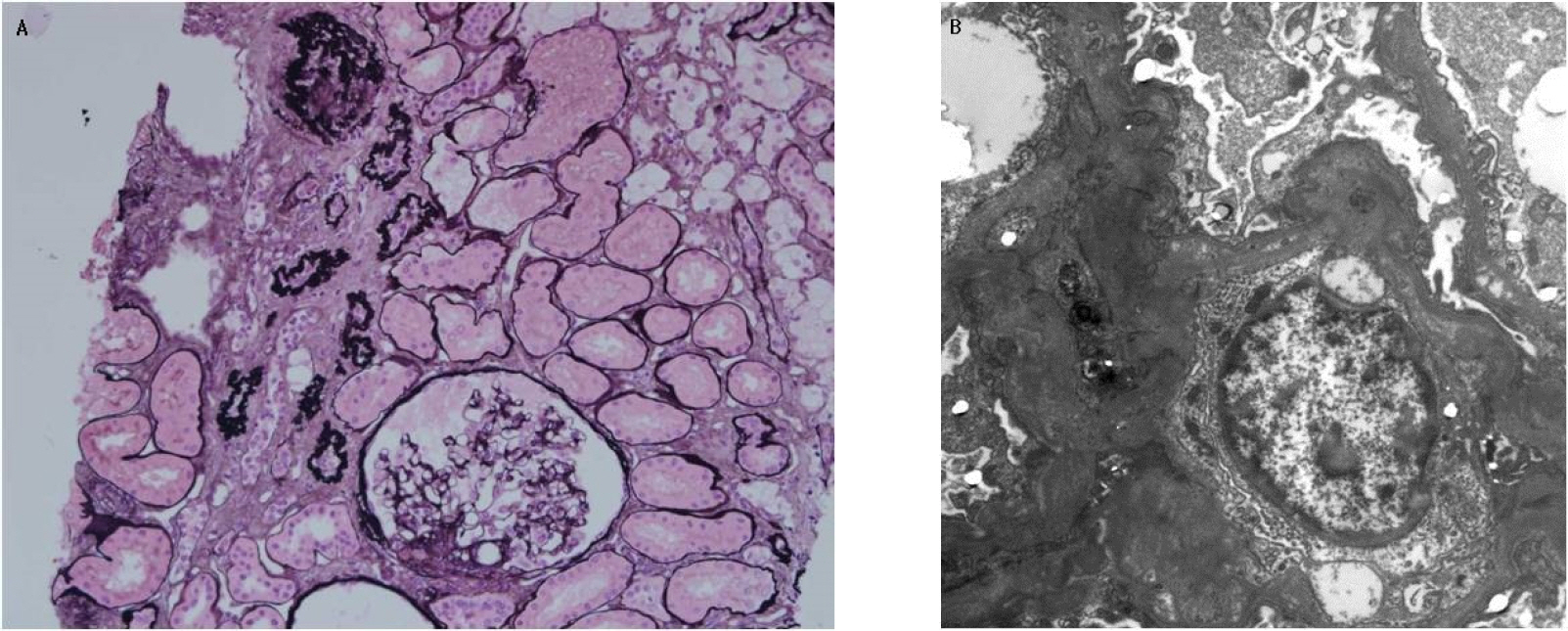

Table 1.Six cases of Turner syndrome with glomerulonephritis
- 1. Elsheikh M, Dunger DB, Conway GS, Wass JA. Turner's syndrome in adulthood. Endocr Rev 2002;23:120–40.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Sybert VP, Mccauley E. Turner's syndrome. N Engl J med 2004;351:1227–38.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Jang GC, Shin HJ, Kim DH. Clinical manifestations according to karyotype in Turner syndrome. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol 2000;5:163–70.
- 4. Goodyer PR, Fong JS, Kaplan BS, Milner LS, Lotan D, Mills M. Turner's syndrome, 46X, delX(P11), Persistent complement activation and membranopro-liferative glomerulonephritis. Am J Nephrol 1982;2:272–5.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Chan PC, Cheng IK, Chan MK. FSGS and mosaic Turner's syndrome. Clin Nephrol 1989;32:149–50.
- 6. Wattad A, Jain J, Kerrigan J, Youngberg G. FSGS and Turner's syndrome. Nephron 1998;80:106.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Suzuki K, Tanaka H, Ito E, Waga S. Therapy-related membranous nephropathy in juvenile idiopathic arthritis with Turner syndrome. Pediatr Int 2004;46:377–9.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Nakamura S, Koshino H, Kon S, Soeda Y, Iwanami N, Ohtsu S, et al. Membranous nephropathy occurred in a patient with Turner's syndrome during rhGH treatment. Kitasato Med J 2013;43:79–81.
- 9. Deegens JK, Dijkman HB, Borm GF, Steenbergen EJ, van den Berg JG, Weening JJ, et al. Podocyte foot process effacement as a diagnostic tool in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 2008;74:1568–76.ArticlePubMed
- 10. McKusick VA. The anatomy of the human genome. Hosp Pract(Hosp Ed) 1981;16:82–100.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Praga M, Morales E, Herrero JC, Perez CA, Dominguez GB, Alegre R, et al. Absence of hypoalbuminemia despite massive proteinuria in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis secondary to hyper-filtration. Am J Kidney Dis 1999;33:52–8.ArticlePubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Renal Problems in Early Adult Patients with Turner Syndrome
Dong Uk Yu, Jae Kyun Ku, Woo Yeong Chung
Childhood Kidney Diseases.2015; 19(2): 154. CrossRef

 KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

