A Case of needle-tract implantation of hepatocellular carcinoma in the ovary after radiofrequency ablation
Article information
Abstract
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), a local ablative modality, is gaining acceptance for the treatment of liver malignancies. Despite a relatively low complication rate, tumor seeding resulting from RFA in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment can occur. A 44-year-old woman was diagnosed with HCC. Spiral computed tomography (CT) revealed a 2.3 × 2.0-cm mass in the S5 segment, which was treated with RFA on May, 2005. Follow-up imaging, performed at 6-month intervals after RFA, showed complete tumor necrosis. In October 2009, CT revealed a heterogeneous mass, 5.7 cm in diameter, in the right ovary. Since the lesion was limited to the right ovary without evidence of spread, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy was performed. Histopathology indicated that the metastatic spread from the HCC to the ovary was positive for hepatocyte-specific antigen on immunohistochemistry. The ovary is a rare site for HCC metastasis. Moreover, needle tract implantation of HCC in the ovary is very rare.
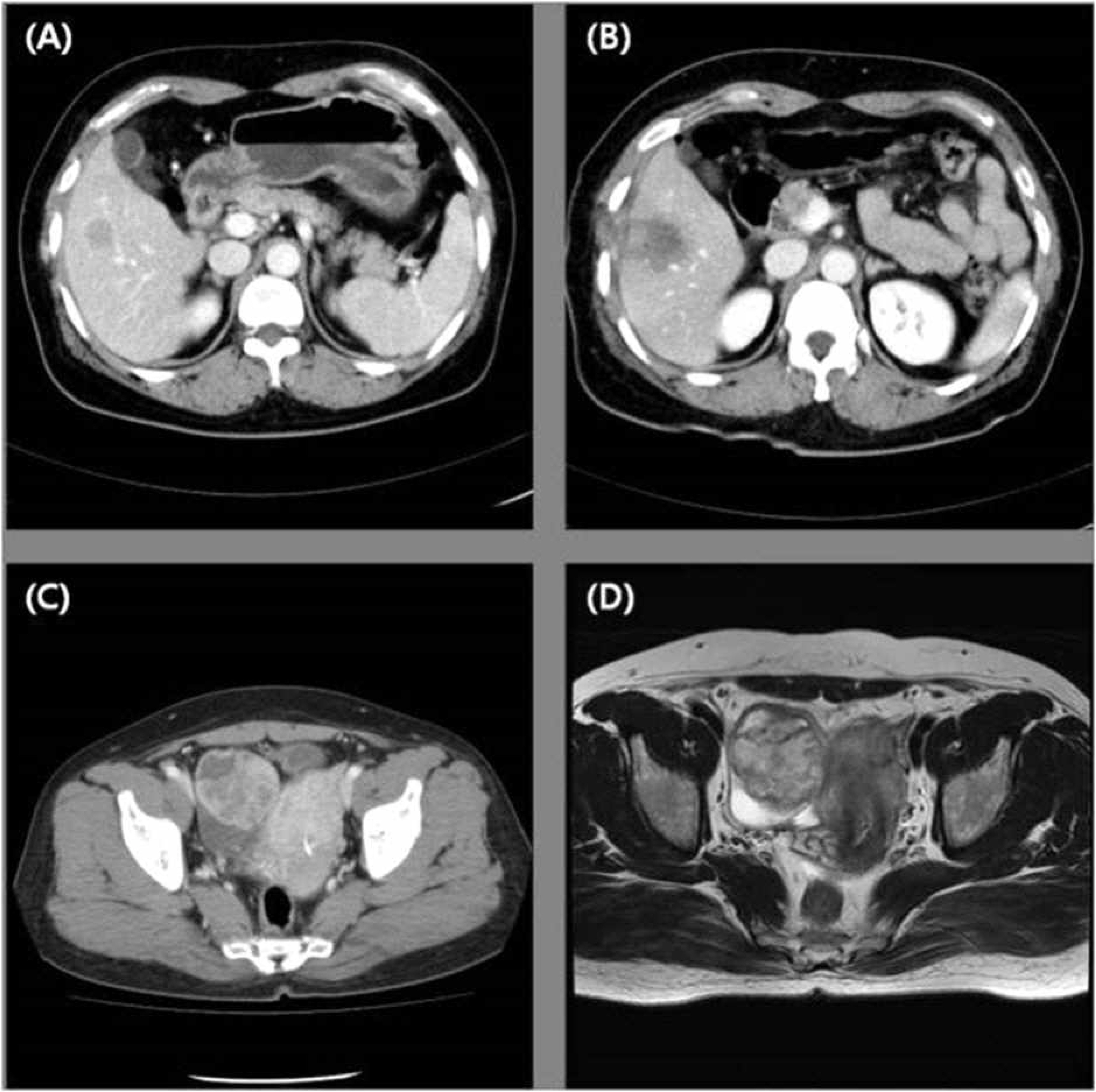
(A) Abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) shows a low- density 2.3 cm mass (before radiofrequency ablation (RFA). (B) low-density lesion on the portal phase in S5 of the liver (post RFA). (C) Abdominopelvic CT reveals a 5.7 cm heterogeneous mass. (D) T2-weighted magnetic resonance image shows a high signal intensity mass in right ovary.
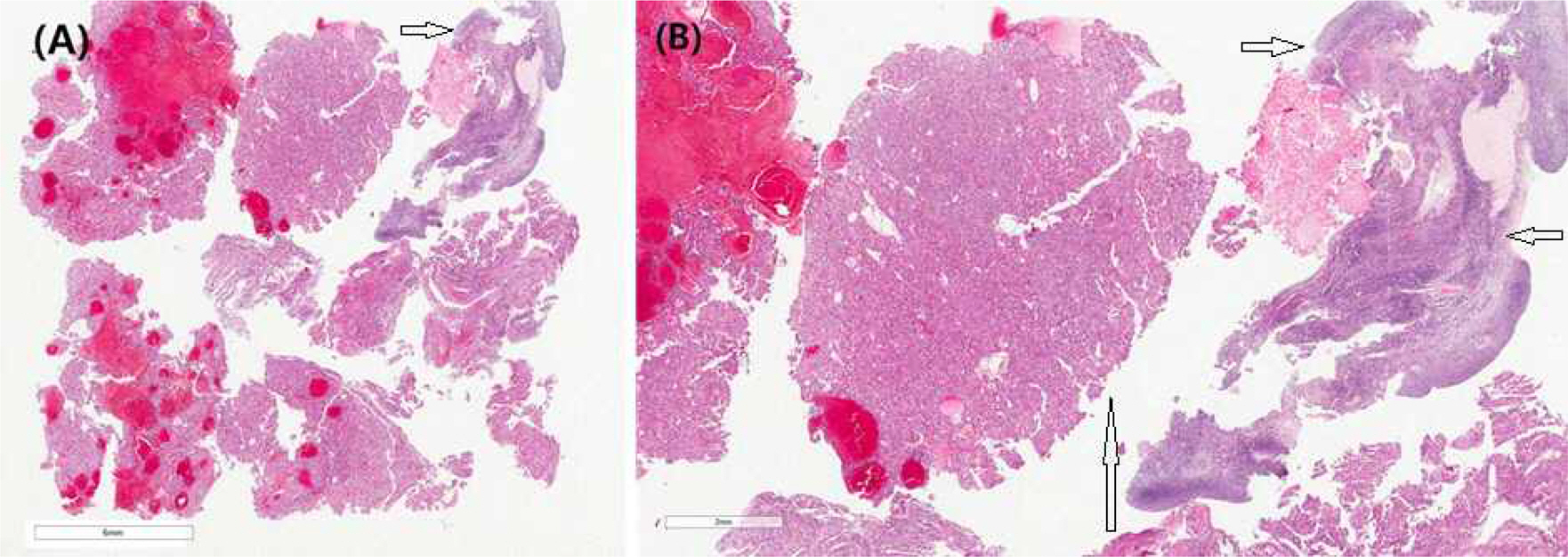
(A) Tissue from ovarian mass (Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining (H-&E) stain, x2). The ovarian mass compose of fragmented ovarian cortex, and tumor mass with hemorrhage. (B) Mid-magnification (H&-E stain, x20). The ovarian mass is of hepatocellular carcinoma with hemorrhage. (Long arrow: HCC, short arrow: Ovary)
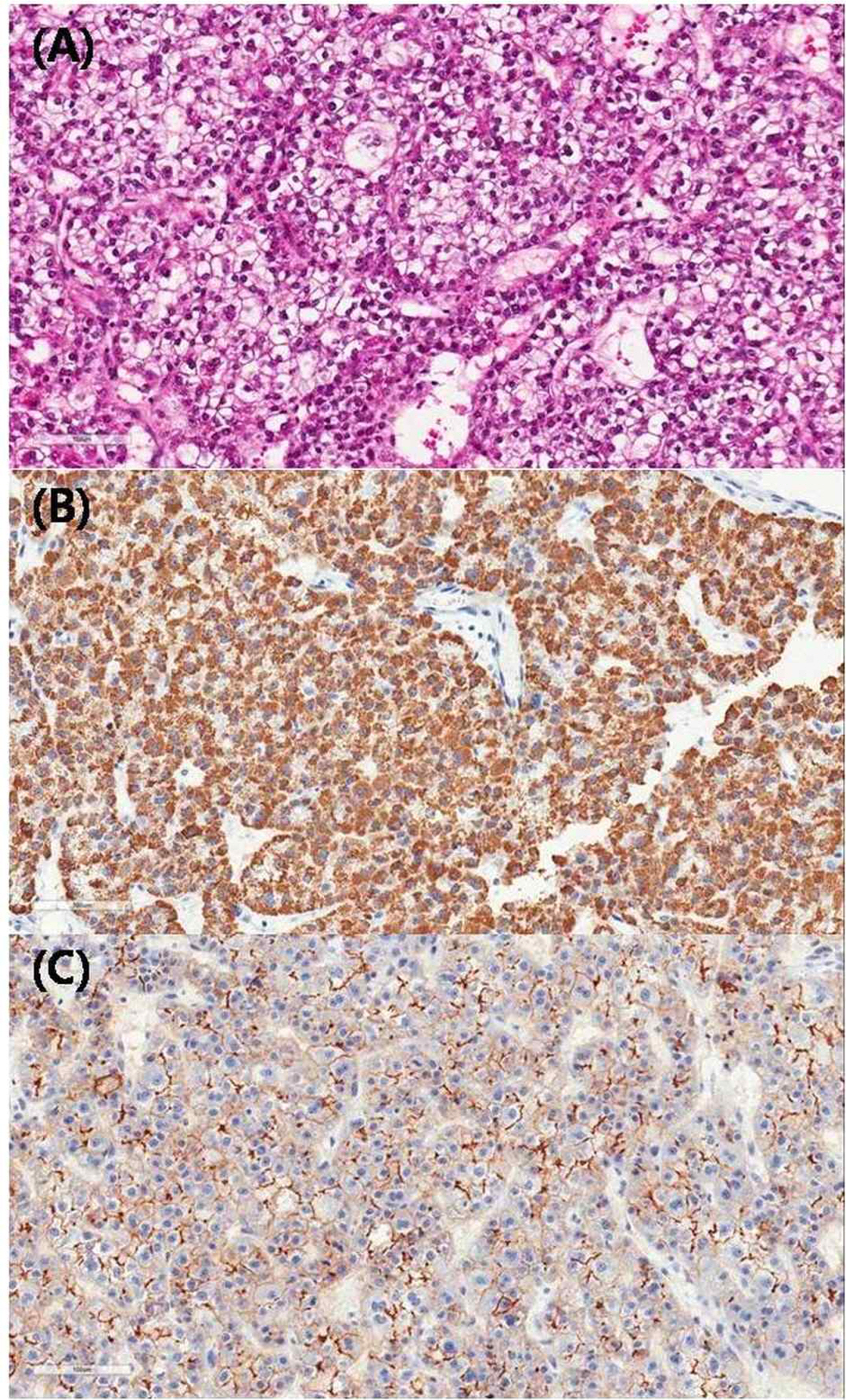
Higher magnification (A, H&-E; B, hepatocyte specific antigen immunohistochemistry (HSA); C, Carcinoembryonic Antigen immunohistochemistry (CEA), x200). (A) The hepatocellular carcinoma metastatic to vary shows thick trabecular and occasionally pseudo glandular architecture, clear cell type and nuclear grade 2/3 (common/worst). (B) Representing clear HAS (+) and (C) bile canalicular type of CEA.