A case report of a carotid space abscess due to extraluminal migration of a fishbone into the deep cervical space
Article information
Abstract
Laryngopharyngeal foreign bodies are among the cases most frequently encountered by otolaryngologists. Most foreign bodies can be easily removed without any complications. However, surgical removal is required in some cases. Therefore, a delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis could cause fatal complications for patients who need a surgical approach. We report a rare case of extraluminal migration of a foreign body to the deep cervical space. The foreign body (a fishbone) was removed by a surgical approach. With a literature review, we also propose an algorithm for the management of suspicious foreign bodies in the neck.
Introduction
The types of laryngopharyngeal foreign bodies could be in various forms, as they are affected by numerous factors such as age, region, or diet [1]. In East Asia including Korea, fishbones show a particularly high incidence among others [2,3]. Most of the laryngopharyngeal foreign bodies not only can be easily found by thorough history taking, physical examination, laryngoscopy, or simple X-ray but also can be removed without any complications. However, in some cases, foreign bodies migrate to extraluminal space such as deep cervical space, which could bring fatal consequences when misdiagnosed. Therefore the possibility of extraluminal migration of foreign bodies should be considered even though they are invisible on laryngoscopy or simple X-ray.
Case
Ethical statements: This report was exempted from approval by the Institutional Review Board of Gyeongsang National University Hospital (IRB No. GNUH 2022-11-013) and written informed consent was waived.
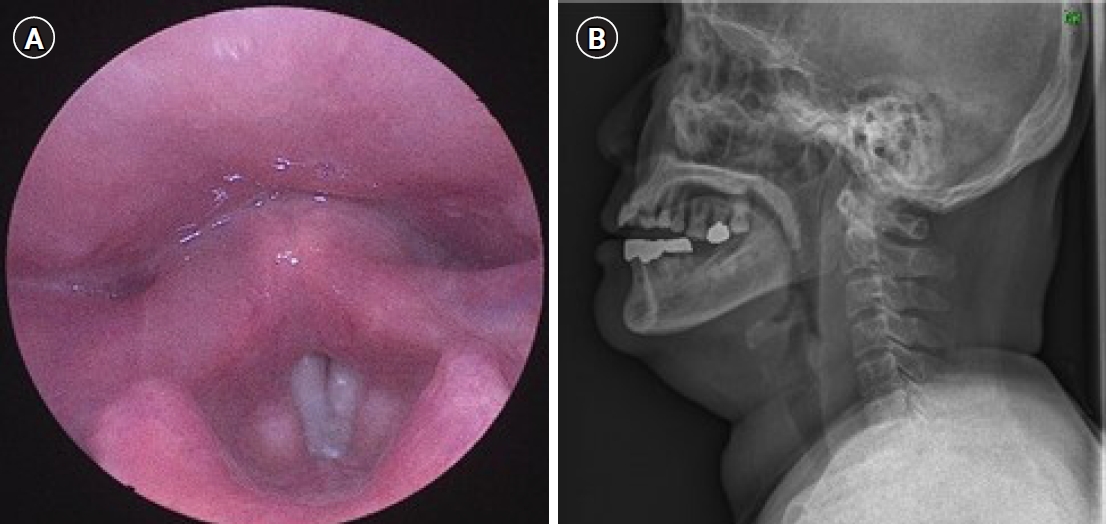
A 60-year-old woman presented to an emergency room with right neck swelling, tenderness, and heating sensation, beginning 2 weeks earlier. According to the patient, neck swelling was gradually aggravated. Physical examination showed diffuse right neck swelling around levels IV, V, and V. Laryngoscopic examination revealed mucosal swelling of the right aryepiglottic fold (Fig. 1A), and an air-tracheogram showed thickening of the soft tissue of the posterior pharynx, and (Fig. 1B). Contrast-enhanced neck computed tomography (CT) revealed an abscess medial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and posterolateral to the thyroid gland, as well as a suspected foreign body-like material (linear-shaped, high density) near the right common carotid artery (Fig. 2). Under general anesthesia, the patient underwent surgical neck exploration through an external neck approach, along with incision and drainage. Massive irrigation, necrotic tissue debridement, and CuraVac insertion were performed, but the severe inflammation and adhesion prevented the detection of the foreign body observed on the CT scan. The patient was subsequently administered intravenous antibiotics for 8 days, followed by surgical neck exploration. After dissection of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, a fishbone, about 3 cm in size, was detected and completely removed (Fig 3).

Representative preoperative computed tomography scan. The imaging findings revealed an abscess formation, medial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and posterolateral to the thyroid gland (arrow). A suspicious foreign body-like material (linear-shaped, high density) was also found near the right common carotid artery (arrowhead). (A, B) Axial views. (C, D) Coronal view.
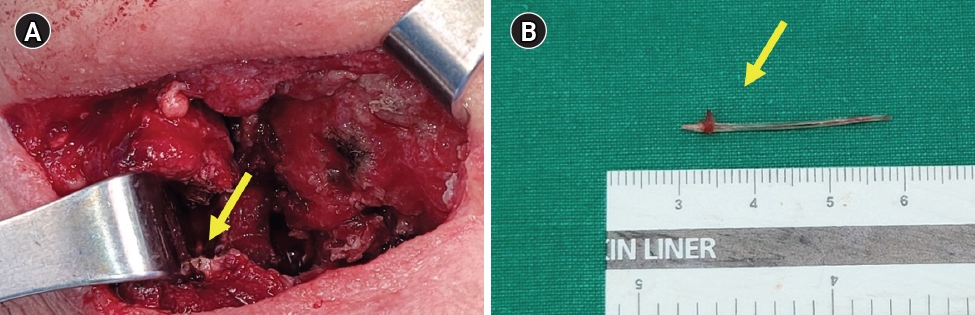
Representative image of the operation field. (A) The sternocleidomastoid muscle was dissected due to severe adhesion and sclerosis throughout the strap muscle, thyroid, and adjacent tissue. (B) A fishbone (arrow) was found on the medial side of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The fishbone was measured to be 3 cm in length.
Discussion
As a majority (69%) of ingested foreign bodies tend to be impacted in the oropharynx and hypopharynx, namely at the tonsil, vallecula, the base of the tongue, or pyriform fossa, most of them can be easily discovered by laryngoscopic examination [4,5]. However, foreign bodies are also often found at the esophagus, and quite a few cases of extraluminal migration of fishbone are also reported: migration of fishbone to the cervical esophagus presenting as a thyroid mass or pyriform sinus foreign body with perforation causing an abscess of the parapharyngeal space [6-8]. If laryngopharyngeal foreign bodies migrate to the cervical space, swelling or tenderness of the neck can be the chief complaints of patients. In that case, accurate diagnosis and prompt surgical intervention should be performed to minimize the damage of complications. Therefore, we invented a schematic algorithm for a suspected foreign body in the neck to avoid misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis (Fig. 4). First of all, thorough history taking and physical examination should precede other examinations. Then, a laryngoscopic examination needs to be performed. If foreign bodies are invisible, an air thacheogram is recommended to evaluate soft tissue swelling and to figure out the presence of foreign bodies. Gastrofiberscopy also needs to be performed to exclude the possibility of esophageal foreign bodies. If there are no abnormal findings, vital signs, laboratory blood test results (leukocytosis or C-reactive protein elevation), and the presence of neck swelling (or mass) should be assessed. Based on these test results, otolaryngologists can decide whether to perform a further radiologic examination or not. CT needs to be performed if extraluminal migration of foreign bodies is suspected. Surgical treatment under general anesthesia can be considered when foreign bodies in the cervical space and complications such as deep neck infection are identified. In conclusion, this report describes a rare case of an extraluminally migrated ingested fishbone, which was successfully removed by an external surgical approach. The whole process from initial history taking to surgical treatment was followed by the algorithm that we invented. When ingested foreign bodies were not found by laryngoscopic examination and gastrofiberscopy, otorhinolaryngologists may misjudge that foreign bodies were already passed through the esophagus as most of the ingested foreign bodies were found in the pharygoesophageal lesion, approximately 86.2%, and 97.1% of esophageal foreign bodies were found by performing gastrofiberscopy [9,10]. However, otorhinolaryngologists should consider the possibility of extraluminal migration of foreign bodies because delayed diagnosis and misdiagnosis could bring fatal consequences. Lastly, sufficient usage of intravenous antibiotics and delayed surgical treatment can be optimal for the case of infectious complications such as deep neck infection due to extraluminal migration of foreign bodies. In the acute inflammatory phase, it is challenging to find foreign bodies in the surgical field due to severe adhesions.
Notes
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Funding
None.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: JJP. Data curation: KJC. Formal analysis: SJW. Investigation: KJC. Methodology: THL. Project administration: JJP. Resources: JJP. Software: THL. Supervision: JJP. Validation: J.J.P. Visualization: THL. Writing - original draft: THL. Writing - review & editing: JJP. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.