A rare case of pure-type embryonal carcinoma in a 75-year-old woman mimicking epithelial ovarian carcinoma
Article information
Abstract
Embryonal carcinoma, a very rare ovarian germ cell tumor, involves pure and mixed phenotypes. Pure-type embryonal carcinoma has never been reported in postmenopausal women. The current case was, thus, misdiagnosed as an epithelial ovarian carcinoma based on radiologic findings. Herein, we describe the case of ovarian embryonal carcinoma in a 75-year-old woman along with a literature review. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were suggestive of epithelial ovarian malignancy associated with endometrioma, including ureteral invasion. The patient underwent complete surgical staging, and a pathologic diagnosis of pure-type embryonal carcinoma was made. The patient’s postoperative course was uneventful, and adjuvant chemotherapy was administered. Embryonal carcinoma in the postmenopausal woman is a clinical challenge owing to the possibility of its misdiagnosis as epithelial ovarian carcinoma. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of pure-type ovarian embryonal carcinoma in a postmenopausal woman, with a description of the clinicopathologic characteristics and review of the relevant literature.
Introduction
Ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs) are considered to be derived from primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonad, making them the most common malignancy of the ovary (1%–2% of all cases) in young women and adolescents [1]. Embryonal carcinoma, a very rare OGCT, most commonly appear as one or more other germ cell tumor types. Cases of pure-type ovarian embryonal carcinoma are very rare [2]. Unilateral oophorectomy is the most common fertility-sparing treatment, followed by combination BEP (bleomycin + etoposide + cisplatin) chemotherapy [1].
Ovarian embryonal carcinoma in postmenopausal women has been reported, and occurs more commonly as mixed germ cell tumor and rarely as pure tumor [3]. The knowledge concerning the development, treatment, and outcomes of postmenopausal embryonal carcinoma is scarce, and the characteristics and prognosis might differ between postmenopausal and premenopausal patients. Herein, we describe the first case of pure-type ovarian embryonal carcinoma in a postmenopausal woman and review the relevant literature.
Case
Ethical statements: This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Pusan National University Hospital (No. 2203-039-113). Informed consent was obtained from the patient agreed to join in the research.
A 75-year-old postmenopausal woman presented with a 1-month history of a palpable mass in the lower abdomen. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed an 11-cm solid cystic mass with heterogeneous signal intensity in the left adnexa, and left hydronephroureterosis showing abrupt narrowing at the ovarian mass level, suggestive of ureteral invasion and epithelial ovarian cancer (Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting & Data System [ORADS] score=5) associated with an endometrioma, such as clear cell or endometrioid carcinoma (Fig. 1). No enlarged lymph nodes or distant metastases were noted in the upper abdomen.
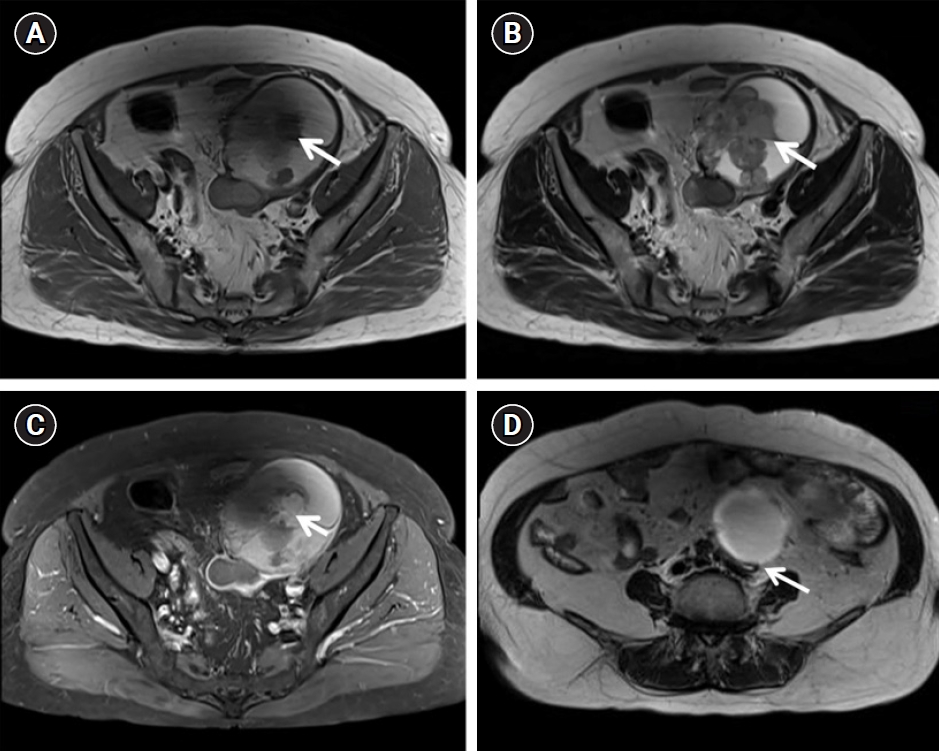
Magnetic resonance images. Axial T1-weighted (A) and T2-weighted (B) images showing a septated hemorrhagic cystic mass with papillary projections (arrow) of the left ovary (ORADS 5). High T1 signal intensity with the T2 dark spot sign, suggestive of epithelial ovarian cancer associated with endometrioma (e.g., clear cell carcinoma or endometrioid carcinoma). (C) Contrast-enhanced axial T-weighted image shows enhancement (arrow) of the papillary projections in the left ovarian tumor. (D) Axial T2-weighted imaging revealed left hydronephrosis (arrow), showing abrupt narrowing at the ovarian mass level suggestive of ureteral invasion. ORADS, Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting & Data System.
Laboratory findings included elevated levels of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH; 372 IU/L [range, 135–225 IU/L]), cancer antigen 125 (17.6 U/mL [range, 0–35 U/mL]) and C-reactive protein (0.68 mg/dL [range, 0–0.5 mg/dL]).
An exploratory laparotomy was performed for staging given the patient’s age. A 12- to 15-cm cystic and solid mass showed an infiltrative growth pattern with adhesions to the adjacent tissue and organs including the bowel, mesentery, ureter, and retroperitoneum. The retroperitoneal mass from the left adnexa was subjected to frozen section biopsy, which revealed malignancy. To confirm oncologic certainty, further dissection of the ureter, extra-fascial total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, omentectomy, appendectomy, pelvic adhesiolysis, and multiple resections of the mesenteric mass, pelvic wall mass, and lymph nodes was performed. The permanent biopsy of the left adnexa and the mass revealed a malignant tumor consistent with embryonal carcinoma confined to the ovary with an intact capsule and no extraovarian spread. The uterus, right ovary, omentum, appendix, mesentery, and pelvic lymph nodes were free of tumor cells. Peritoneal washings were also negative for malignant cells, confirming stage IA disease.
Microscopically, the tumor had a predominantly solid pattern of highly anaplastic cells and numerous mitotic figures. The excised mass showed immunoreactivity for CD30, p53, and WT1, and focal positivity for panCK (Fig. 2).
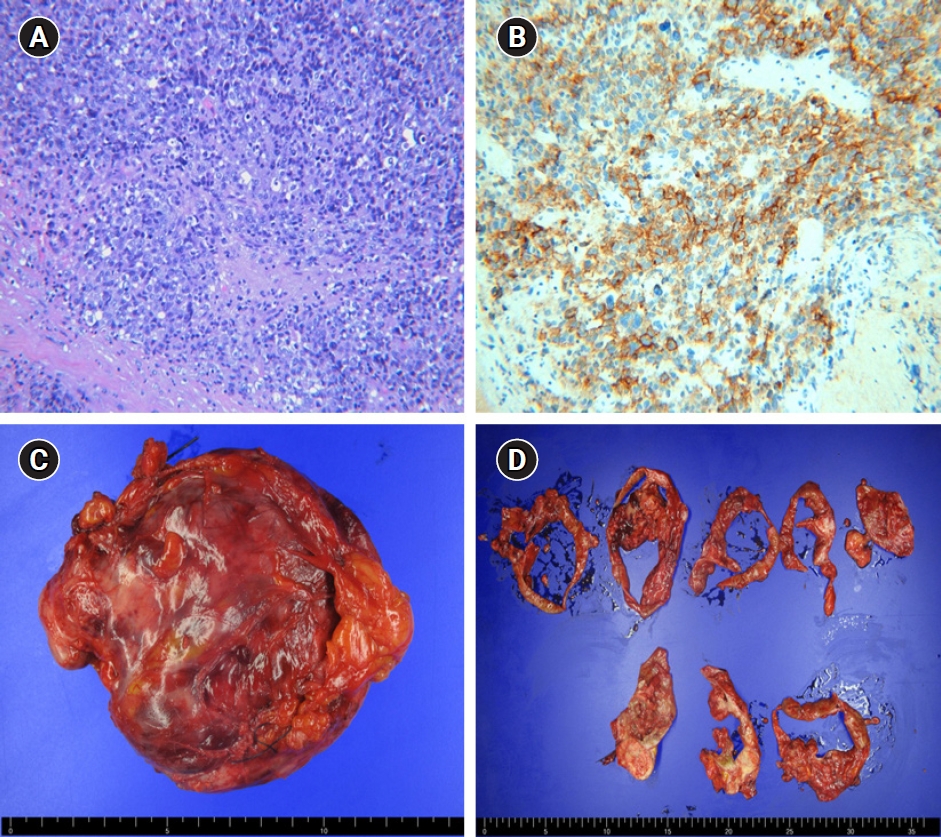
Pathologic findings. (A) Tumor showing a predominantly solid pattern of highly anaplastic tumor cells and numerous mitotic figures (H&E, x200). (B) The tumor cells tested positive for CD30, a specific marker of embryonal carcinoma (x200). (C) Gross findings. A 12- to 15-cm cystic and solid mass was confined to the ovary with an intact capsule. (D) Cutting sections of the tumor.
Postoperative laboratory tests for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) showed normal serum levels: 2.1 IU/mL (range, 0–10.0 IU/mL) and 1.08 mIU/mL (range, 0–5 mIU/mL), respectively. The LDH level decreased to 200 IU/L (range, 135–225 IU/L). The patient’s postoperative care was uneventful. Subsequently, the patient underwent 4 courses of BEP. She has been recurrence-free for 12 months.
Discussion
Embryonal carcinoma was first described in 1976 by Kurman and Norris [4]. Patients with ovarian embryonal carcinoma may present with abdominal pain, a palpable mass, and abdominal distension; irregular heavy bleeding may occur due to abnormal hormonal secretion. Our patient had no symptoms other than a palpable mass. Most of these tumors are stage I and confined to one ovary [4]. The overall 5-year survival rates for embryonal carcinoma in the first reported series of 15 patients were reportedly 39% and 50% for all stages and stage I, respectively [4]. However, BEP chemotherapy for adjuvant therapy improved mean survival rates exceeding 90% [5].
Immunohistochemistry is important to the diagnosis of embryonal carcinoma. CD30 is consistently positive in most embryonal carcinoma cases. The tumor cells can produce AFP and β-hCG and contain giant or syncytiotrophoblastic cells with necrosis and hemorrhage that stain positive for cytokeratin and hyaline bodies in premenopausal patients [2]. In the current case, the excised mass tested positive for CD30, p53, and WT1 and focal positivity for panCK. The tumor showed a predominantly solid pattern of highly anaplastic tumor cells and numerous mitotic figures without necrosis and hemorrhage and other histological types could not be seen from pathological findings; thus, it could be diagnosed as pure-type.
The treatment of embryonal carcinoma in younger women is unilateral oophorectomy and combination chemotherapy with BEP. In the case of embryonal carcinoma in young women, similar to other germ cell tumors, the tumor did not show an infiltrative growth pattern or form adhesions with adjacent organs, making it less difficult to perform debulking surgery and sensitive to chemotherapy [7,8]. In contrast, it showed a more infiltrative growth pattern in postmenopausal patients; therefore, the survival rate of germ cell tumors in postmenopausal women is reportedly lower than that of women of reproductive age or adolescents [9]. Therefore, ovarian preservation is not recommended for postmenopausal OGCT patients and a thorough staging operation is necessary [10]. On radiologic imaging, in younger patients, malignant germ cell tumors are generally large and nonspecific with a complex but predominantly solid form and ascites with hemorrhage and necrosis on imaging, while the invasion of other pelvic organs is more likely to occur in postmenopausal patients [11]. On MRI, an incorrect initial diagnosis was made of epithelial ovarian malignancy (ORADS score 5) associated with endometrioma such as clear cell or endometrioid carcinoma. Moreover, other findings included hydronephrosis showing abrupt narrowing at the ovarian mass level suggestive of ureteral invasion. This is the first report of the MRI findings of pure-type embryonal carcinoma in a postmenopausal woman.
Laboratory tests for AFP, β-hCG, LDH, and other tumor markers may contribute to the preoperative diagnosis and choice of therapeutic effects. The disease may be associated with high AFP and β-hCG levels, but such a pattern is not absolute and different associations could be observed, especially when the embryonal carcinoma is pure-type (Table 1) [6].

The current patient versus the most recent case of a postmenopausal embryonal carcinoma patient and the previously published case of pure-type embryonal carcinoma in a premenopausal woman
The present case is the first of pure-type embryonal carcinoma of the ovary. Table 1 compares the current case versus the previously published postmenopausal embryonal carcinoma patient and the most recent case of pure-type in a premenopausal woman. As OGCTs including ovarian embryonal carcinoma in postmenopausal women might have different characteristics and prognoses from those of premenopausal women, more research and case reports are needed to better understand this rare entity.
Notes
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Funding
This work was supported by a 2-Year Research Grant of Pusan National University.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: DSS. Data curation: KUC, NKL. Formal analysis: EJK, YJS. Funding acquisition: DSS. Investigation: HBJ. Supervision: KHK. Validation: KHK. Writing - original draft: HBJ. Writing - review & editing: ETK. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
